| CPC B60L 58/40 (2019.02) [B60L 50/50 (2019.02); H01M 8/0494 (2013.01); H01M 10/0525 (2013.01); H01M 10/425 (2013.01); H01M 10/44 (2013.01); H01M 10/46 (2013.01); H01M 16/006 (2013.01); H01M 2220/20 (2013.01); H01M 2250/20 (2013.01)] | 16 Claims |
|
1. An apparatus for managing power of a fuel cell, the apparatus comprising:
a power conversion device configured to convert a high voltage into a low voltage, which is lower than the high voltage, and to supply the converted low voltage to a low voltage battery;
a cooling device configured to flow a coolant to cool the power conversion device; and
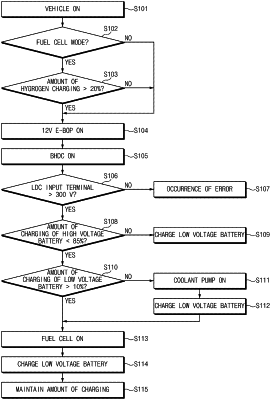
a controller configured to determine whether or not to drive the cooling device based on a remaining state of charge (SOC) of the low voltage battery, and to control the cooling device to be driven to cool the power conversion device based on a determination result of whether to drive the cooling device,
wherein the power conversion device includes:
a bidirectional high voltage DC-DC converter (BHDC) configured to drop a regenerative power to charge a high voltage battery, an operating voltage of which is higher than that of the low voltage battery, or to boost a power of the high voltage battery to supply the boosted power to an electrical load; and
a low voltage DC-DC converter (LDC) configured to convert an output power of the BHDC into a low voltage to charge the low voltage battery, and
wherein the controller drives the BHDC, and then drives the LDC to charge the low voltage battery when 1) a voltage at an input terminal of the LDC is higher than a certain voltage and 2) a remaining SOC of the high voltage battery is greater than or equal to a second SOC.
|
|
8. A method for managing power of a fuel cell, the method comprising:
controlling driving of a power conversion device configured to convert a high voltage into a low voltage, which is lower than the high voltage, and supplying the converted low voltage to a low voltage battery;
determine whether or not to drive a cooling device configured to flow a coolant to cool the power conversion device, based on a remaining state of charge (SOC) of the low voltage battery;
controlling the cooling device to be driven to cool the power conversion device based on a determination result of whether or not to drive the cooling device;
dropping, by a bidirectional high voltage DC-DC converter (BHDC), a regenerative power to charge a high voltage battery, an operating voltage of which is higher than that of the low voltage battery, or boosting, by the BHDC, a power of the high voltage battery to supply the boosted power to an electrical load;
converting, by a low voltage DC-DC converter (LDC), an output power of the BHDC into a low voltage to charge the low voltage battery; and
driving the BHDC, and then driving the LDC to charge the low voltage battery when 1) a voltage at an input terminal of the LDC is higher than a certain voltage and 2) a remaining SOC of the high voltage battery is greater than or equal to a second SOC.
|