| CPC B41F 17/001 (2013.01) [A61M 39/0208 (2013.01); C09D 11/02 (2013.01); A61M 2039/0238 (2013.01); B41M 1/10 (2013.01); B41M 1/22 (2013.01); B41M 7/00 (2013.01); B41M 7/009 (2013.01)] | 6 Claims |
|
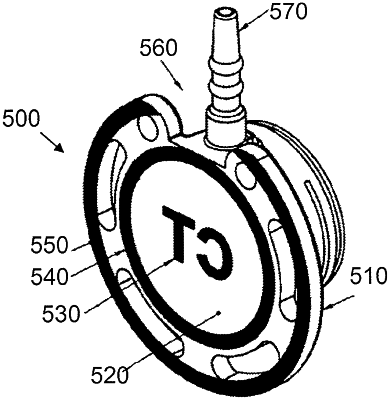
1. A venous access port, comprising:
a housing that includes an interior fluid reservoir;
a septum; and
a discharge port extending from the reservoir;
wherein a bottom surface of the housing is printed with at least one X-ray discernable indicium by the steps of:
positioning the venous access port on a jig, wherein the jig comprises a plate having at least one recess configured to hold the venous access port;
applying radiopaque marking fluid to a surface of a plate comprising one or more etchings having a depth between 0.0001 inches and 0.003 inches, wherein the radiopaque marking fluid comprises a clear ink and tungsten particulates having at least one particulate size more than 1 micron and no more than 5 microns, a ratio of the clear ink and the tungsten particulates being determined according to a material of the venous access port on which the radiopaque marking fluid is to be applied;
depositing the radiopaque marking fluid onto a surface of the plate around the one or more etchings and into the one or more etchings by placing an inverted cup containing the radiopaque marking fluid onto the surface of the plate over the one or more etchings, the inverted cup comprising a ring that is compressed against the plate due to an attraction by a plurality of magnets disposed on a riser of the cup when the inverted cup is placed onto the surface of the plate, the ring being a structure that circumvents a perimeter of the cup and the riser being a member positioned at a central point of the cup, wherein the plurality of magnets comprises at least four magnets positioned concentrically within the ring and located equidistant from each other;
wiping the radiopaque marking fluid deposited onto the surface of the plate around the one or more etchings off the surface of the plate around the one or more etchings by translating the cup so as to cause the ring to slide along the surface of the plate away from the one or more etchings, thereby exposing the radiopaque marking fluid deposited within the one or more etchings to air to allow the radiopaque marking fluid to achieve a sufficient level of tackiness; and
picking up some of the radiopaque marking fluid deposited within the one or more etchings using a silicone pad and transferring the picked up radiopaque marking fluid to the venous access port, the silicone pad having a firmness to facilitate transfer of as much of the radiopaque marking fluid deposited within the one or more etchings to the venous access port that will adhere to the venous access port;
wherein the steps of applying, exposing, and transferring are an application of the radiopaque marking fluid, the application being repeated to achieve an amount of the radiopaque marking fluid on the venous access port having at least a predetermined radiopacity;
wherein the printed radiopaque marking fluid indicates by visual inspection of the printed venous access port prior to being implanted into a patient, and by X-ray examination after being implanted into a patient, that the venous access port is capable of high pressure injection.
|