| CPC B22F 9/24 (2013.01) [A61K 9/5115 (2013.01); A61K 9/5192 (2013.01); B22F 1/054 (2022.01); B22F 1/0545 (2022.01); B22F 1/056 (2022.01); B22F 1/102 (2022.01); B22F 2009/245 (2013.01); B82Y 5/00 (2013.01); B82Y 15/00 (2013.01); B82Y 40/00 (2013.01)] | 10 Claims |
|
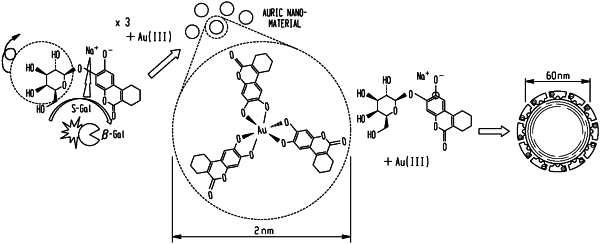
1. A method of making reduced metal nanoparticles, comprising:
mixing a reactive reducing agent with a metal salt in a solution at a temperature of 4-100° C., wherein the reducing agent comprises 3,4-cyclohexenoesculetin-β-D-galactopyranoside or 3,4-cyclohexenoesculetin-β-D-glucoside, or a water-soluble salt thereof; and
forming reduced metal nanoparticles in the solution.
|