| CPC B03C 7/04 (2013.01) [B03C 3/08 (2013.01); B03C 3/09 (2013.01)] | 10 Claims |
|
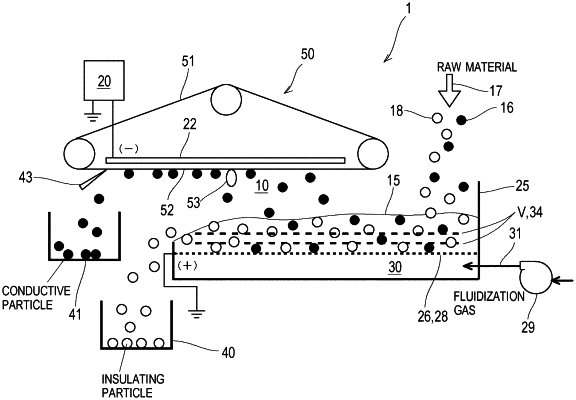
1. An electrostatic separator that separates conductive particles from raw materials including the conductive particles and insulating particles,
the electrostatic separator comprising:
a container in which a raw material layer including the raw materials is located;
a gas dispersion plate located at a bottom portion of the raw material layer;
at least one vibrating body located in the raw material layer, the at least one vibrating body being flush with the gas dispersion plate or being located above the gas dispersion plate;
a fluidization gas supplier that supplies a fluidization gas that is introduced from a bottom portion of the container into the raw material layer and flows upward in the raw material layer through the gas dispersion plate;
an upper electrode located above the raw material layer;
a lower electrode located in the raw material layer, the lower electrode being flush with the gas dispersion plate or being located above the gas dispersion plate;
a power supply that applies a voltage between the upper electrode and the lower electrode such that one of the upper electrode and the lower electrode becomes a negative electrode, the other becomes a positive electrode, and an electric field is generated between these electrodes;
a capturer that captures the conductive particles that have flown out of a surface of the raw material layer toward the upper electrode; and
at least one intermediate electrode located in the raw material layer and above the lower electrode, wherein
a potential difference between the upper electrode and the intermediate electrode is equal to or less than a potential difference between the upper electrode and the lower electrode.
|