| CPC A63F 13/75 (2014.09) [A63F 13/79 (2014.09); G06N 20/00 (2019.01); A63F 2300/535 (2013.01); A63F 2300/5586 (2013.01)] | 17 Claims |
|
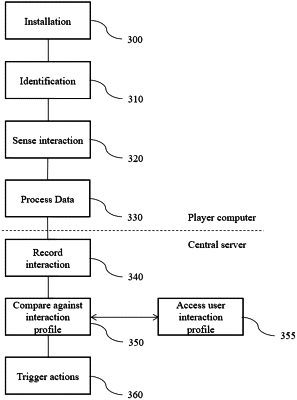
1. A computer-implemented method for detection of fraudulent behavior of a player in an online video game, wherein the fraudulent behavior is one of replacement of the player by another player or the use of performance-enhancing software or hardware by the player the method comprising:
collecting at a personal computer device a plurality of interaction data relating to a plurality of interactions of the player with a plurality of peripheral devices connected to the personal computer device;
transmitting the interaction data to a central computer server;
performing at the central computer server a comparison between the transmitted interaction data and a general player interaction profile stored in a player interaction database;
performing at the central computer server a comparison between the transmitted interaction data and one or more specific player interaction profiles stored in the player interaction database to verify an identity of one of the player and the another player;
identifying a risk of fraudulent behavior based on the comparison between the transmitted interaction data and the stored player interaction profile as well as one or more specific player interaction profiles; and
receiving from the central computer server a message indicative of the risk of fraudulent behavior, wherein
at least one of the general player interaction profile or the one or more specific player interaction profile is derived from at least one of a statistically based normal interval level or a model derived from machine learning;
the interaction data comprises movement distances of a movable one of the peripheral devices moved by the player; and
the normal interval level is between a maximum usual movement distance and a minimum usual movement distance and wherein the comparison to identify the risk of fraudulent behavior is determined by comparing one of more of the movement distances to determine whether they fall within the normal interval level.
|