| CPC A61M 5/1723 (2013.01) [G16H 20/17 (2018.01); A61M 2202/07 (2013.01); A61M 2205/18 (2013.01); A61M 2205/3569 (2013.01); A61M 2205/50 (2013.01); A61M 2205/502 (2013.01); A61M 2205/52 (2013.01); A61M 2205/581 (2013.01); A61M 2205/583 (2013.01); A61M 2230/201 (2013.01)] | 12 Claims |
|
1. A device, comprising:
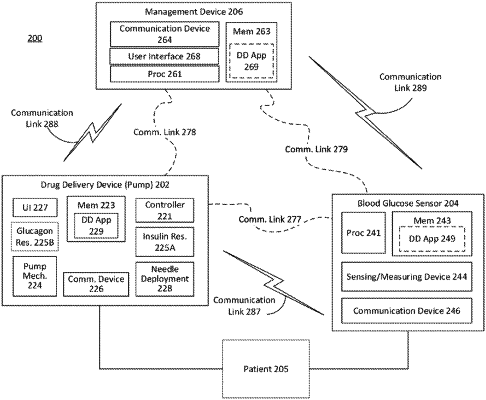
a communication interface with a glucose monitor for enabling glucose level readings of a user from the glucose monitor to be communicated to the device;
a storage for storing insulin delivery history and/or glucagon delivery history to the user and a carbohydrate ingestion history of the user;
a delivery device interface with a delivery device for delivery of the insulin and/or glucagon to the user; and
processing logic for:
determining a required insulin on board (IOB) of the user to reach a target glucose level of the user given a current glucose level of the user;
determining a current IOB of the user;
calculating a difference between the required IOB of the user to reach the target glucose level and the current IOB of the user;
where the difference is positive,
determining a limit of device compensation as a maximum automated insulin action that may result from automated insulin deliveries by the device in a period in view of constraints;
determining whether the limit of device compensation is enough to reach the target glucose level of the user given the current glucose level and the current IOB of the user;
where it is determined that the limit of device compensation is not enough to reach the target glucose level of the user, determining a hyperglycemic action threshold as a sum of the hyperglycemic threshold and a maximum amount of a glucose level of the user that can be compensated by the device in a time period in view of the limit of device compensation for the time period,
comparing the current glucose level of the user to the hyperglycemic action threshold; and
where the current glucose level of the user is greater than the hyperglycemic action threshold, triggering a preventive measure to reduce the glucose level of the user.
|