| CPC A61M 5/1723 (2013.01) [G16H 10/40 (2018.01); G16H 20/10 (2018.01); G16H 20/17 (2018.01); A61M 2205/3569 (2013.01); A61M 2205/3584 (2013.01); A61M 2205/502 (2013.01); A61M 2205/52 (2013.01); A61M 2230/201 (2013.01)] | 15 Claims |
|
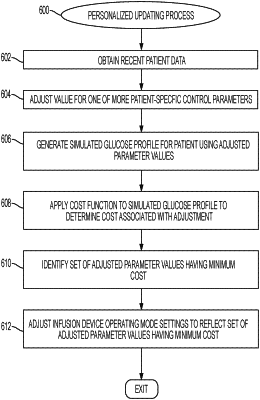
1. A method of automatically adjusting a control parameter for an operating mode of a medical device, the method comprising:
obtaining, by one or more processors, data pertaining to a physiological condition of a patient during operation of the medical device;
determining, by the one or more processors, a plurality of adjusted values for the control parameter to be optimized using a cost function based at least in part on the data, the control parameter being a proportional-integral-derivative (PID) gain coefficient value, a PID time constant, an insulin limit, or a pharmodynamical time constant;
for each of the plurality of adjusted values for the control parameter, determining, by the one or more processors, a respective cost associated with the respective adjusted value for the control parameter based at least in part on the data using the cost function, resulting in a plurality of costs associated with each of the plurality of adjusted values, wherein the cost function disproportionately penalizes negative excursions relative to a target range for the physiological condition, and wherein the cost function disproportionately penalizes the negative excursions relative to the target range by including a first penalty term dependent on time spent outside of the target range, and a second penalty term, different from the first penalty term, dependent on time spent below a lower bound of the target range;
identifying, by the one or more processors, from among the plurality of adjusted values, an optimized value from among the plurality of adjusted values, wherein the optimized value has a minimum cost associated therewith from among the plurality of costs; and
controlling, by the one or more processors, fluid delivery of the medical device to deliver fluid to the patient according to the control parameter at the optimized value.
|