| CPC A61M 15/0068 (2014.02) [A61M 15/0021 (2014.02); A61M 15/009 (2013.01); H04Q 9/00 (2013.01); A61M 2202/064 (2013.01); A61M 2205/3334 (2013.01); A61M 2205/3584 (2013.01); A61M 2205/581 (2013.01); A61M 2205/582 (2013.01); A61M 2205/583 (2013.01); H04Q 2209/40 (2013.01)] | 17 Claims |
|
1. An electronic system comprising:
an inhaler device for dispensing a medicament formulation in aerosol or dry powder form and
an external device which is configured to receive data communicated from the inhaler device,
wherein the inhaler device comprises:
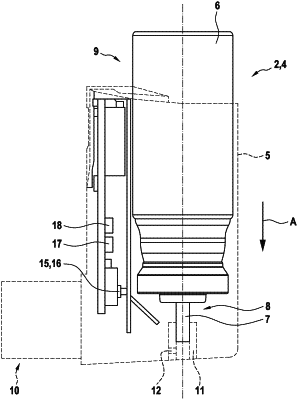
a mouthpiece,
a flow rate sensor for sensing a flow rate of an inhalation flow which is caused by a patient upon inhalation through the mouthpiece and in which the medicament formulation is entrained or dispensed,
an actuation sensing device having at least one actuation sensor which is configured to sense preparatory steps of the inhaler device in order to prepare a use of the inhaler device and/or to sense the actuation of the inhaler device in order to dispense the medicament formulation, the at least one actuation sensor and the flow rate sensor being configured to generate sensor signals and
a wireless transmitting unit for communicating data related to the sensor signals to the external device,
wherein the electronic system further comprises:
an instruction unit configured to generate visual, tactile and/or acoustic instructions in order to support the patient during use of the inhaler device and
an evaluation unit for evaluating the sensor signals and/or the communicated data, the evaluation unit being configured to:
evaluate a use of the inhaler device by comparing measurements taken by the sensors with the instructions given to the patient and/or with predefined data,
wherein
the evaluation unit is further configured to:
autonomously adapt the point in time at which the instructions are outputted in order to ensure that the measurements taken by the sensors correspond to a use of the inhaler device by the patient according to the predefined data,
verify whether an adaptation of timing of the instructions leads to a use of the inhaler device by the patient according to the predefined data during a subsequent use of the inhaler device by comparing measurements taken by the sensors during the subsequent use of the inhaler device with the predefined data and
evaluate how single adaptations of the instructions in timing impact on individual use of the inhaler device by the patient by comparing measurements taken by the sensors during the subsequent use of the inhaler device with measurements taken from the sensors during the previous use of the inhaler device.
|