| CPC A61B 5/352 (2021.01) [A61B 5/346 (2021.01); A61B 5/726 (2013.01); G01R 23/16 (2013.01); G16H 40/67 (2018.01); G16H 50/70 (2018.01); G06F 17/10 (2013.01); G16H 50/20 (2018.01)] | 7 Claims |
|
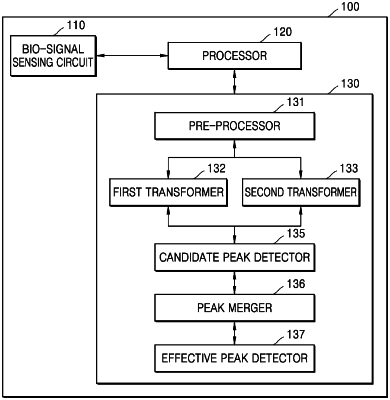
1. A bio-signal measurement apparatus comprising:
a bio-signal sensing circuit configured to sense an electrocardiogram signal using an electrode attached to a body;
a processor;
a memory that stores executable instructions that, when executed by the processor of the bio-signal measurement apparatus, facilitate performance of operations, the operations comprising:
converting the electrocardiogram signal to a first transform signal by performing first-level wavelet transform;
converting the electrocardiogram signal to a second transform signal by performing second-level wavelet transform;
detecting first candidate peaks based on a magnitude of the first transform signal and detecting second candidate peaks based on a magnitude of the second transform signal;
calculating an average value of time values of the first candidate peaks and the second candidate peaks included in a first window having a predetermined time interval based on a heart rate or an R-R interval and setting the average value of time values as a first average peak time value in the first window;
calculating a first complexity value of the first transform signal and a second complexity value of the second transform signal for the first window including the first average peak time value, using a complexity calculation algorithm based on a turning point ratio (TPR), wherein the first complexity value and the second complexity value become higher as a number of turning points in the first window is greater, and the TPR corresponds to a value indicating a ratio of a location of a turning point indicating a change in magnitude of two adjacent pieces of data at a particular time point with respect to a total data length, and the turning point refers to a point at which a direction of data values is changed;
determining the first average peak time value as a peak occurring time value when the first complexity value and the second complexity value exceed a pre-set critical complexity level; and
detecting effective peaks in the electrocardiogram signal as peaks occurring at the peak occurring time value; and
wherein the first-level wavelet transform is performed in an order different from an order applied to the second-level wavelet transform, and
the order applied to the first-level wavelet transform and the order applied to the second-level wavelet transform are a changeable value.
|