| CPC A61B 5/14532 (2013.01) [A61B 5/1455 (2013.01); A61B 5/6826 (2013.01); A61B 5/6838 (2013.01); A61B 5/7225 (2013.01); G16Z 99/00 (2019.02); A61B 2562/0238 (2013.01); A61B 2576/00 (2013.01)] | 12 Claims |
|
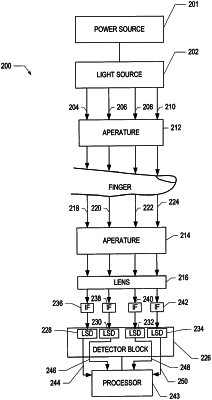
1. A system for detecting glucose in a biological sample, comprising:
a processor programmed to calculate a change in a light absorption caused by blood in the biological sample and configured to receive an output photocurrent signal from at least one photocurrent signal generating light detector and calculate an attenuance attributable to blood in the biological sample present in a target area with a signal-to-noise ratio based on the received output photocurrent signal, and determine a blood glucose level associated with the biological sample present in the target area based on the calculated attenuance, wherein the processor is configured to calculate a peak-to-valley height of the change in light absorption due to blood in the biological sample in relationship to time, which is a function of a standard deviation of a logarithm of a time dependent output current divided by a proportionality constant, wherein the processor is programmed to reduce noise without increasing data acquisition time by using the standard deviation.
|