| CPC A61B 34/10 (2016.02) [G06T 7/74 (2017.01); G09B 19/003 (2013.01); A61B 2034/104 (2016.02); A61B 2034/105 (2016.02); G06T 2207/20021 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30101 (2013.01)] | 13 Claims |
|
1. A method for matching an actual surgical image and a 3D-based virtual surgical simulation environment, which is performed by an apparatus, the method comprising;
setting point-of-interest (POI) information during surgery at each of surgery steps in a pre-stored surgical image obtained by performing surgery the same as the actual surgical image;
generating a virtual pneumoperitoneum model of a patient, which is configured to be used for the 3D-based virtual surgical simulation environment, by performing:
realizing a blood vessel having the same state as the state of the blood vessel in the patient's actual pneumoperitoneum status;
capturing an Early Arterial Phase (EAP) image and a portal venous phase (PP) image, using the EAP image to divide or restore an artery on a Computed tomography (CT) image, and using the PP image to divide or restore a vein on the CT image;
additionally dividing or restoring main portions of the artery when the vein is divided or restored, to adjust a location of the artery so as to match major portions of the artery on the vein; and
matching the vein and the artery depending on a major portion of the artery, wherein the major portion of the artery is POI information, and is a bifurcation of the artery;
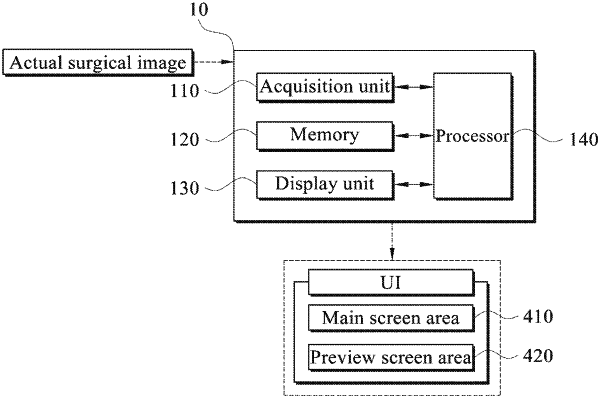
matching the POI information with the virtual pneumoperitoneum model of the patient, wherein the virtual pneumoperitoneum model is displayed on a user interface (UI);
recognizing a real-time surgery step of the actual surgical image and determining a location of the POI information for the respective recognized surgery step; and
obtaining and displaying image information, which is captured by moving a location of an endoscope inserted into the virtual pneumoperitoneum model to the same location as the determined location of the POI information, through the UI.
|