| CPC A61B 3/102 (2013.01) [A61B 3/0008 (2013.01); A61B 3/103 (2013.01); A61B 3/12 (2013.01)] | 12 Claims |
|
1. An ophthalmologic apparatus comprising:
a fixation projection system configured to project fixation light flux onto a fundus of a subject's eye;
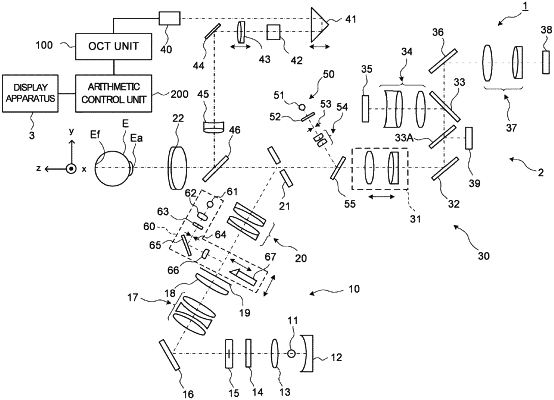
an interference optical system including an optical scanner and configured to split light from light source into measurement light and reference light, to irradiate the subject's eye with the measurement light deflected by the optical scanner, and to detect interference light between returning light of the measurement light from the subject's eye and the reference light;
a controller configured to perform OCT measurement on a first scan region and a second scan region, which are different from each other in the subject's eye, by controlling the interference optical system in a state where a projected position of the fixation light flux on the fundus is fixed: and
an optical path length difference changing unit configured to change a difference of optical path lengths between an optical path of the measurement light and an optical path length of the reference light, wherein
the controller is configured to change the difference of the optical path lengths by controlling the optical path length difference changing unit in accordance with a position of a scan region in the subject's eye, and to change a reference position of a measurement range in a depth direction of the OCT measurement on the subject's eye.
|