| CPC A61B 17/00 (2013.01) [A61B 1/24 (2013.01); A61C 1/16 (2013.01); A61C 3/00 (2013.01); A61B 2017/00429 (2013.01); A61B 2017/00862 (2013.01); A61C 2202/00 (2013.01)] | 19 Claims |
|
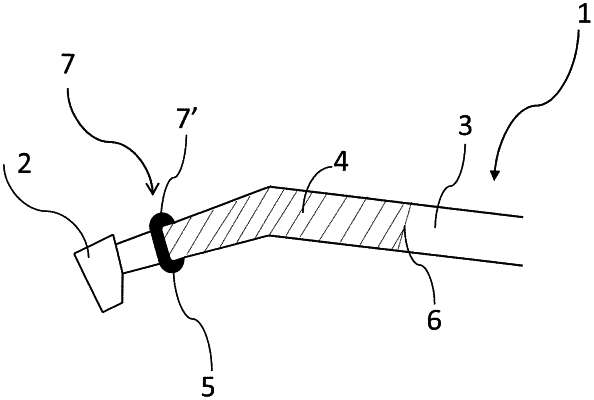
1. A dental instrument comprising:
an elongated medical instrument comprising an elongated element, the elongated element of the elongated medical instrument having a gripping area and a head element being attached to an end of the elongated element; and
a medical instrument grip device for the elongated medical instrument, the medical instrument grip device comprising an open tubular element of elastic material;
wherein the tubular element is open in both longitudinal ends and is configured to switch between a rolled up state and a fully unrolled state,
wherein the tubular element is further configured such that the head element of the elongated element may be forced through an inner opening of the tubular element when the tubular element is stretched and in the rolled up state, and to create a tight fit around the gripping area of the elongated element when the tubular element is in the fully unrolled state,
wherein a cross sectional circumferential distance of the tubular element before stretching is equal or smaller than cross sectional circumferential distances of the gripping area of the elongated element onto which the tubular element is to be fitted,
wherein a ratio between the circumferential distance of the tubular element before stretching and the circumferential distance of the tubular element after reaching a stretched expanded state when forcing the head element of the elongated element through the inner opening, is between 1:1.1 and 1:5,
wherein the material is chosen such that the tubular element has an ability to contract back to a relaxed state, or at least contract enough to allow the tubular element to make a tight fit on to the gripping area of the elongated element, and
wherein the circumferential distance of an onset of the gripping area of the elongated element, dgrip, is smaller than the circumferential distance of the head element of the elongated element, dhead.
|