| CPC H04N 25/702 (2023.01) [H04N 25/53 (2023.01); H04N 25/75 (2023.01); H04N 25/134 (2023.01)] | 10 Claims |
|
1. A cone-rod dual-modality neuromorphic vision sensor, comprising a first preset quantity of voltage-mode active pixel sensor (APS) circuits and a second preset quantity of current-mode APS circuits, wherein
the voltage-mode APS circuit comprises a first-type photosensitive device, the first-type photosensitive device is configured to obtain a target light signal, extract a light signal of a specified frequency band from the target light signal, and convert the light signal of the specified frequency band into a first-type current signal, and the voltage-mode APS circuit is configured to output, based on the first-type current signal, a target voltage signal representing light intensity information in the target light signal; and
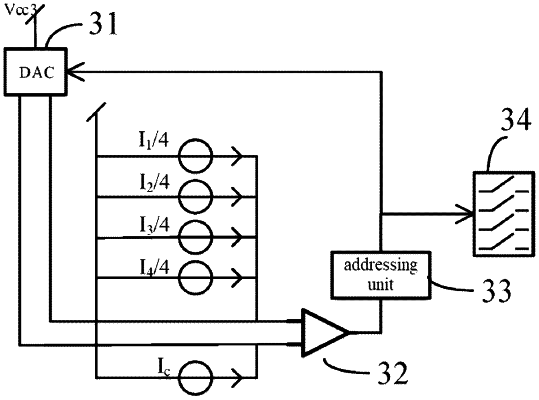
the current-mode APS circuit comprises a second-type photosensitive device, the second-type photosensitive device is configured to obtain the target light signal, and convert the target light signal into a second-type current signal, and the current-mode APS circuit is configured to output, based on the second-type current signal, a specified digital signal representing light intensity gradient information in the target light signal.
|