| CPC G16B 20/20 (2019.02) [C12Q 1/6809 (2013.01); C12Q 1/689 (2013.01); G16B 20/00 (2019.02); G16B 20/10 (2019.02); G16B 30/10 (2019.02); C12Q 2600/112 (2013.01); C12Q 2600/154 (2013.01); G16B 30/00 (2019.02)] | 29 Claims |
|
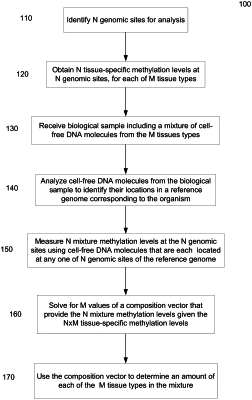
1. A method of analyzing a biological sample of an organism, the biological sample including a mixture of cell-free DNA molecules from M tissues types, M being greater than two, the method comprising:
identifying N genomic sites, wherein, for one or more other samples, a first set of the N genomic sites each have a coefficient of variation of methylation levels of at least 0.15 across the M tissue types and each have a difference between a maximum and a minimum methylation level for the M tissue types that exceeds 0.1, the first set including at least 10 genomic sites;
for each of the M tissue types:
obtaining N tissue-specific methylation levels at the N genomic sites, N being greater than or equal to M, wherein the tissue-specific methylation levels form a matrix A of dimensions N by M;
analyzing a plurality of cell-free DNA molecules from the biological sample, the plurality of cell-free DNA molecules being at least 1,000 cell-free DNA molecules, wherein analyzing each of the plurality of cell-free DNA molecules includes:
identifying a location of the cell-free DNA molecule in a reference genome corresponding to the organism, wherein locations of a number of the plurality of cell-free DNA molecules that depends on N for a given accuracy are identified;
measuring N mixture methylation levels at the N genomic sites using a first group of the plurality of cell-free DNA molecules that are each located at any one of N genomic sites of the reference genome corresponding to the organism, wherein the N mixture methylation levels form a methylation vector b;
solving for a composition vector x that provides the methylation vector b for the matrix A; and
for each of one or more components of the composition vector x:
using the component to determine an amount of a corresponding tissue type of the M tissue types in the mixture.
|