| CPC G06F 7/582 (2013.01) [G01V 3/12 (2013.01); G06F 7/68 (2013.01)] | 7 Claims |
|
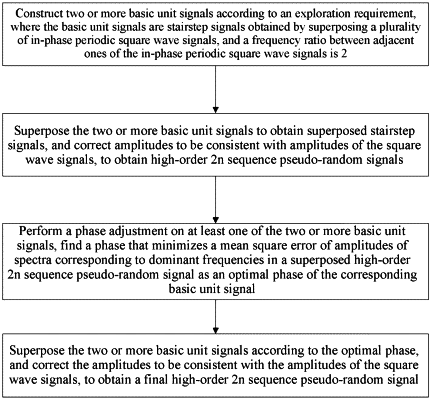
1. A method for generating a high-order pseudo-random electromagnetic exploration signal, the method comprising:
constructing two or more basic unit signals according to an exploration requirement, wherein the basic unit signals are stairstep signals obtained by superposing a plurality of in-phase periodic square wave signals, and a frequency ratio between adjacent ones of the plurality of periodic square wave signals is 2; and
superposing the two or more basic unit signals to obtain superposed stairstep signals, and correcting amplitudes to be consistent with amplitudes of the periodic square wave signals, to obtain high-order 2n sequence pseudo-random signals,
the method further comprising:
performing a phase adjustment on at least one of the two or more basic unit signals, and finding a phase that minimizes a relative mean square (RMS) error of amplitudes of spectra corresponding to dominant frequencies in a superposed high-order 2n sequence pseudo-random signal as an optimal phase of the corresponding basic unit signal; and
superposing the two or more basic unit signals according to the optimal phase, and correcting the amplitudes to be consistent with the amplitudes of the periodic square wave signals, to obtain final high-order 2n sequence pseudo-random signals, wherein
a method for finding the optimal phase comprises:
for the basic unit signal on which the phase adjustment is performed, dividing a phase radian π in a half period into N parts, to obtain phase-changed basic units π/N;
adjusting one phase-changed basic unit in every one time, and recording the RMS error of the amplitudes of the spectra corresponding to the dominant frequencies in the superposed high-order 2n sequence pseudo-random signal; and
drawing a variation curve of the RMS error with a phase, and finding a phase that minimizes the RMS error as the optimal phase of the basic unit signal.
|