| CPC G02B 6/255 (2013.01) [G02B 6/2551 (2013.01); G02B 6/32 (2013.01)] | 13 Claims |
|
1. A process for splicing a glass fiber onto an optical component, said method comprising:
disposing a cross-sectional surface of said glass fiber and a surface of said optical component at a distance from one another; and
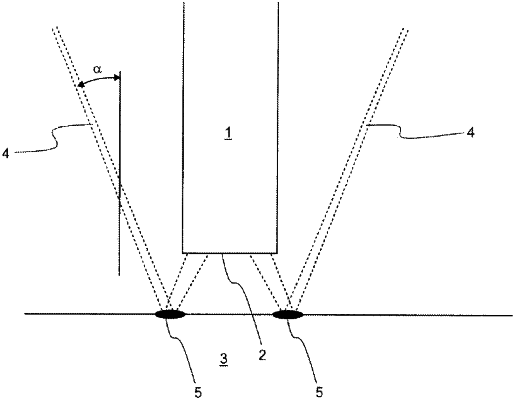
directing an annular-shaped laser beam at said optical component surface so that the laser beam is aiming toward but not focused on said optical component surface and also does not directly hit said glass fiber,
wherein an angle of incidence of the laser beam as it is aiming toward said optical component surface is between 10 degrees and 60 degrees;
and the distance between said glass fiber cross-sectional surface and said optical component surface and the angle of incidence are chosen such that said laser beam irradiates a portion of an annular zone of said optical component surface until said annular zone of the optical component begins to soften, and
said laser beam is reflected from said optical component surface toward the glass fiber cross-sectional surface, and warms said glass fiber cross-sectional surface without said cross-sectional surface softening, so that said glass fiber cross-sectional surface and said optical component surface are spliced together.
|