|
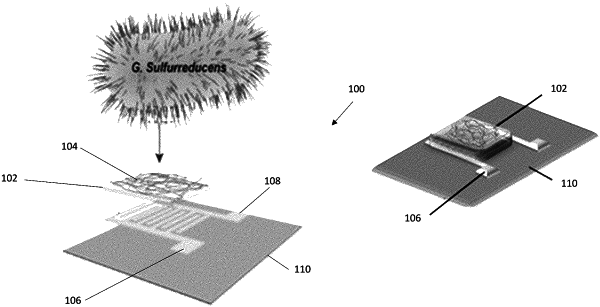
1. A gas sensor comprising: a biomaterial comprising electrically-conductive protein nanowires, wherein the protein nanowires comprise a structure assembled from protein monomers having an amino acid sequence selected from SEQ ID NO:1-SEQ ID NO:33 and variants thereof; and at least two electrodes in operative arrangement with the protein nanowires and configured to provide a signal indicative of a change in conductivity of the protein nanowires, the conductivity of the protein nanowires being responsive to a change in concentration of a gas exposed to the biomaterial.
|