| CPC C25B 11/091 (2021.01) [C25B 1/04 (2013.01)] | 17 Claims |
|
1. An electrode, comprising an electrically conductive substrate coated with an electrocatalyst, the electrocatalyst comprising:
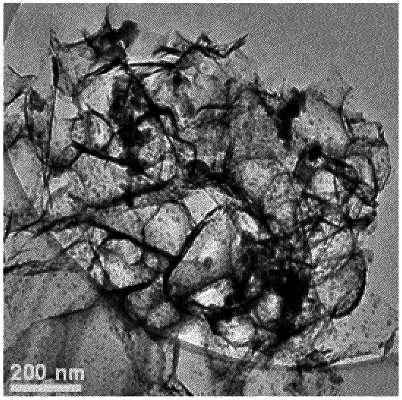
nanoparticles of an iron phosphide; and
carbon nanosheets as a catalyst support, the carbon nanosheets having no nitrogen or phosphorus doping, and the carbon nanosheets being interconnected with covalent carbon-carbon bonds,
wherein the carbon nanosheets branch by at least partially peeling so that a single nanosheet branches into multiple nanosheets each individually having a continuous structure but covalently connected to one or more core or nucleus nanosheets,
wherein the nanoparticles have an average diameter in the range of from 3 to 30 nm, and the carbon nanosheets have a thickness of no more than 3 nm,
wherein the molar ratio of the nanoparticles of the iron phosphide to the carbon nanosheets is in a range of from 0.15 to 0.3,
wherein the electrode has a BET surface area in a range of from 140 to 200 m2/g,
wherein the electrode has a hydrogen evolution reaction turnover frequency in a range of from 0.90 to 0.30 s1,
and wherein the electrode has an overpotential in a hydrogen evolution reaction to produce a current density of 10 mA/cm2 in acidic conditions in a range of from 50 to 104 mV.
|