| CPC C01B 32/198 (2017.08) [A01N 43/90 (2013.01); A01N 59/00 (2013.01); A61L 27/08 (2013.01)] | 16 Claims |
|
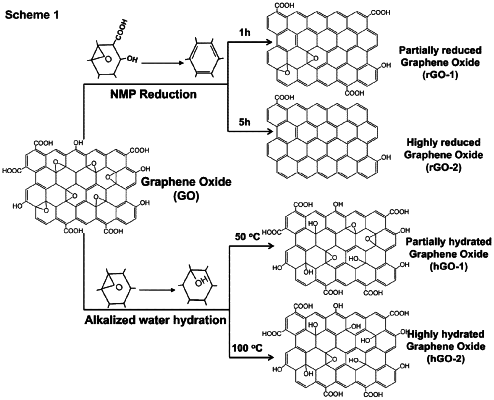
1. A method of killing and/or inhibiting the growth and/or proliferation of a microorganism said method comprising contacting said microorganism, or a biofilm containing said microorganism with a hydrated graphene oxide (hGO) film disposed on a glass, metal, or polymer solid surface, where said hydrated graphene oxide film has increased carbon radical (·C) density as compared to pristine graphene oxide (GO), wherein said increased carbon radical density is characterized by:
i) an EPR spectrum showing a single resonance peak of it-conjugated carbon radical; and
ii) an atomic percent concentration of epoxide (C—O—C) groups lower than pristine graphene oxide; and
iii) an atomic percent concentration of C—OH groups for said hGO at least twice the atomic percent concentration of C—OH groups on pristine graphene oxide as determined by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS); and
wherein said hydrated graphene oxide film disposed on said surface has increased antimicrobial activity as compared to a pristine graphene oxide film.
|