| CPC B60W 60/0059 (2020.02) [B60W 40/09 (2013.01); B60W 40/12 (2013.01); B62D 15/021 (2013.01); B60W 2420/403 (2013.01); B60W 2510/0657 (2013.01)] | 18 Claims |
|
1. A method comprising:
determining input torque values obtained from a steering torque sensor associated with a steering input mechanism of a vehicle, wherein the input torque values are obtained over a period of time;
determining road disturbances using a road disturbance model;
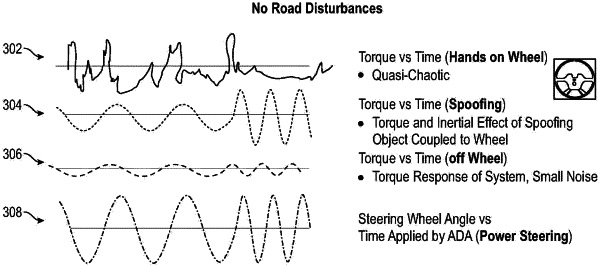
filtering noise from the input torque values, the noise being inferred from the road disturbance model, the noise being created from road and/or environmental conditions;
applying a driver model that is indicative of human driver hands-on-wheel behaviors;
determining when input torque values are indicative of a spoof or human interaction with the steering input mechanism using the input torque values, the road disturbance model, and the driver model; and
executing a remediating measure when the input torque values are indicative of the spoof.
|