| CPC B60G 17/02 (2013.01) [B60G 17/0165 (2013.01); B60G 17/019 (2013.01)] | 17 Claims |
|
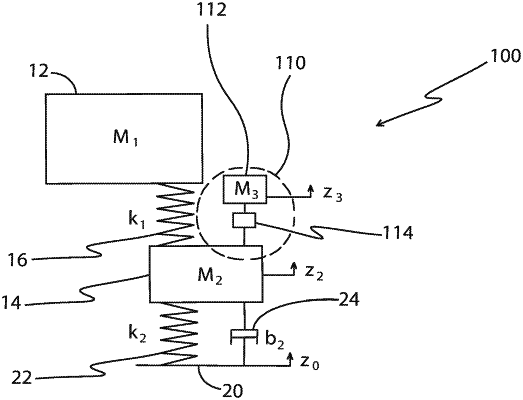
1. An active suspension control system for a motor vehicle including a sprung mass, an unsprung mass coupled to the sprung mass and at least one wheel and tire combination coupled to the unsprung mass such that road terrain movement acting on the at least one wheel and tire combination along a z-axis induces movement of the unsprung mass along the z-axis which, in turn, induces movement of the sprung mass also along the z-axis, the active suspension control system comprising:
an active mass damper configured to be mounted to the unsprung mass, the active mass damper including a damper mass and an actuator responsive to a drive signal to cause the damper mass to move relative to the unsprung mass in a direction having a movement component acting along the z-axis,
an actuator driver responsive to a control signal to produce the drive signal,
at least one sensor configured to produce at least one sensor signal indicative of the component of movement of the unsprung mass along the z-axis,
a control circuit,
a memory having instructions stored therein executable by the control circuit to cause the control circuit to produce the control signal based on the at least one sensor signal to control movement of the damper mass so as to cancel, or at least reduce, movement of the unsprung mass in response to the road terrain-induced movement acting on the unsprung mass via the at least one wheel and tire combination, and
a force actuator coupling the unsprung mass to the sprung mass, the force actuator comprising a magnet coupled directly to one of the sprung mass and the unsprung mass, and an actuator including a housing attached to the other of the sprung mass and the unsprung mass,
wherein the magnet of the force actuator is disposed within and movable relative to the force actuator housing,
and wherein the actuator of the force actuator is configured to be responsive to a force actuator drive signal to cause the magnet of the force actuator to move relative to the force actuator housing to deliver a force between the sprung and unsprung masses along the z-axis which cancels, or at least reduces, movement of the sprung mass relative to the unsprung mass.
|