| CPC A61N 5/1039 (2013.01) [G06T 7/0012 (2013.01); G16H 20/40 (2018.01); G16H 50/30 (2018.01); G06T 2207/20081 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30096 (2013.01)] | 17 Claims |
|
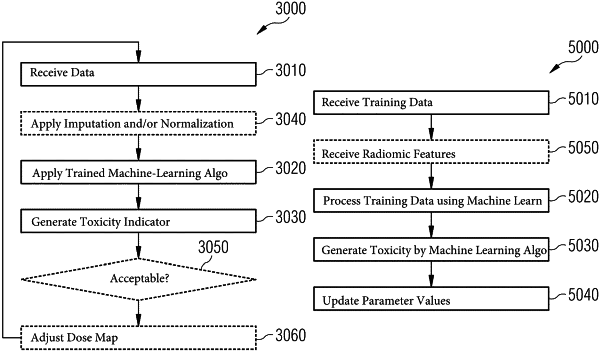
1. A computer-implemented method for predicting risks of radiation-induced toxicity associated with a radiotherapy treatment of a target region of a patient, the method comprising:
receiving data associated with a region of interest comprising the target region, wherein the received data comprises a predefined dose map of the radiotherapy treatment and pre-radiotherapy-treatment imaging data of the region of interest;
applying a trained machine-learning algorithm to the received data, the trained machine-learning algorithm having been trained by: (1) processing multiple instances of training data by the machine-learning algorithm, the multiple instances of training data associated with the region of interest comprising the target region and multiple instances of reference data, each one of the multiple instances of the reference data corresponding to a respective instance of the training data, wherein each one of the multiple instances of the training data comprises the dose map of the radiotherapy treatment and the pre-radiotherapy-treatment imaging data of the region of interest, wherein each instance of the multiple instances of the reference data comprises at least one diagnosed toxicity indicator indicative of diagnosed risks of radiation-induced toxicity, and (2) updating parameter values of the machine-learning algorithm based on a comparison between diagnosed toxicity indicators and corresponding estimated toxicity indicators by the machine-learning algorithm; and
generating, by the trained machine-learning algorithm, at least one toxicity indicator based on the received data, wherein the at least one toxicity indicator is indicative of the risks of the radiation-induced toxicity.
|