| CPC A61M 60/191 (2021.01) [A61M 60/289 (2021.01); A61M 60/468 (2021.01); A61M 2205/04 (2013.01)] | 8 Claims |
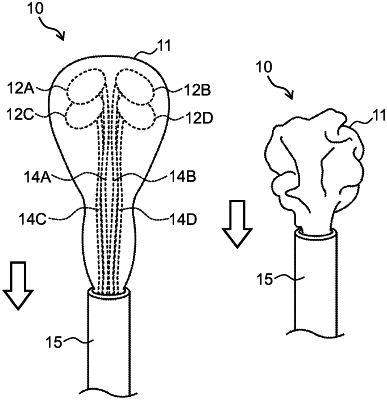
|
1. A cardiac output support apparatus comprising:
a diaphragm that is configured to fit an external shape of a lower heart part of a target person and, wherein the diaphragm is composed of a flexible membrane that is responsive to a gas pressure;
a plurality of compression balloons that are located at specified positions of an inner wall surface of the diaphragm, wherein the compression balloons are positioned opposite to atriums and ventricles of a heart, respectively when the lower heart part is covered and wrapped with the diaphragm;
an air pressure actuator that is configured to press a gas into the diaphragm;
a left actuator and a right actuator that are each configured to eject or absorb a fluid to or from the compression balloons, respectively; and
a tubular joint with a hollow part in which the diaphragm and each of the compression balloons are collectively stuffed, wherein the diaphragm is stuffed into the hollow part of the tubular joint with reference to a mark assigned to a top end of the tubular joint by defining a positional relationship between respective compression balloons,
wherein, in a state where the top end of the tubular joint is interposed in a chest of the target person, the tubular joint is located at the lower heart part, and the mark is positioned in conformity with the atriums and the ventricles, the air pressure actuator is configured to:
push the diaphragm out from the top end of the tubular joint while the gas is pressed into the diaphragm,
simultaneously cause the diaphragm to start flexing to cover and wrap the lower heart part, and
stop pressing the gas into the diaphragm at a time point where the compression balloons are positioned at the atriums and the ventricles of the heart, respectively; and
wherein the left actuator and the right actuator are each configured to support a pumping function of the heart by alternately repeating:
an ejecting operation that fills each of the compression balloons with the fluid, wherein the ejecting operation causes each compression balloon to expand, and
an absorbing operation that causes each respective compression balloon to discharge the fluid and contract.
|