| CPC A61B 8/485 (2013.01) [G01S 7/52022 (2013.01); G01S 7/52042 (2013.01); A61B 8/483 (2013.01)] | 14 Claims |
|
1. A method of performing shear wave elastography in tissue, comprising:
providing a single array transducer;
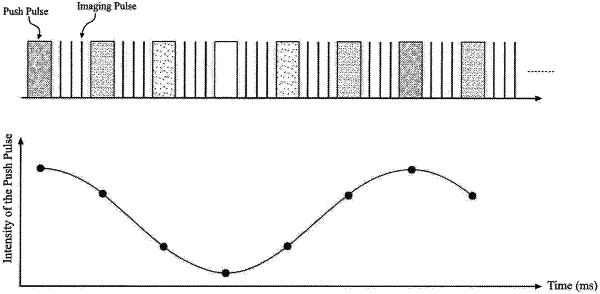
transmitting successively a series of ultrasound push pulses in the tissue around a region of interest (ROI) using the single array transducer, acoustic intensities of the push pulses being sinusoidally modulated to follow a sinusoidally changing pattern with a sinusoidal modulation frequency;
each push pulse generating an acoustic radiation force that pushes the tissue thus creating an individual shear wave having an amplitude and propagating through the tissue, the amplitude of each individual shear wave changing positively proportionally to the intensities of the push pulses, the successively created individual shear waves with different amplitudes summing together to form a continuous, narrowband summed shear wave with a single frequency, the single frequency being the same as the sinusoidal modulation frequency of the push pulses.
|