| CPC A61B 5/4519 (2013.01) [A61B 5/0048 (2013.01); A61B 5/1107 (2013.01); A61B 5/4041 (2013.01); A61B 5/7246 (2013.01); A61B 5/725 (2013.01); A61B 5/7257 (2013.01); A61B 5/726 (2013.01); A61B 5/7267 (2013.01); A61B 5/746 (2013.01); A61B 90/08 (2016.02); A61B 2560/06 (2013.01)] | 21 Claims |
|
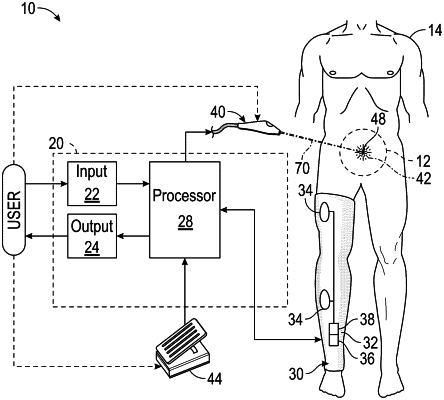
1. A method for detecting an artificially induced neuromuscular response in a subject, the method comprising:
receiving, by a processor, a mechanomyography (MMG) output signal from a mechanical sensor in contact with a muscle of the subject;
applying, by the processor, one or more conditioning filters to the MMG output signal to generate a conditioned signal;
analyzing, by the processor, the conditioned signal to identify one or more candidate waveforms, each candidate waveform meeting one or more analog or digital signal characteristic criteria associated with an artificially induced neuromuscular response;
comparing, by the processor, a first candidate waveform to a second candidate waveform to determine a degree of similarity between the first and second candidate waveforms;
providing an alert to a user that indicates detection of the artificially induced neuromuscular response when the degree of similarity exceeds a predetermined threshold.
|