| CPC A61B 5/1106 (2013.01) [A61B 5/0002 (2013.01); A61B 5/746 (2013.01)] | 8 Claims |
|
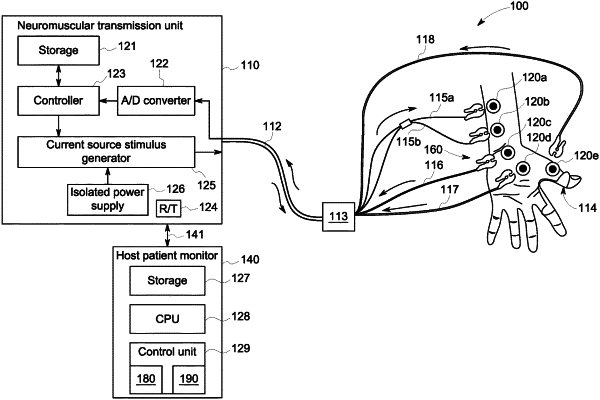
1. A method of monitoring depth of muscle relaxation of a patient, the method comprising:
applying, by an electrode, a series of stimulations to a nerve of a patient and measuring muscle responses thereto;
based on the muscle responses, determining, by a processor, at least one of a maximal stimulus current, a supramaximal stimulus current, and a submaximal stimulus current for the patient, wherein the maximal stimulus current is a current at which a maximal muscle response is produced from stimulating the nerve, the supramaximal stimulus current is greater than or equal to the maximal stimulus current, and the submaximal stimulus current is less than the maximal stimulus current;
applying, by the electrode, a first set of stimulations to the nerve of the patient and measuring first muscle responses to the first set of stimulations; and
selecting, by the processor, one of the supramaximal stimulus current and the submaximal stimulus current for a subsequent series of stimulations based on the first muscle responses to the first set of stimulations, the selecting comprising:
determining whether the first muscle responses to the first set of stimulations are at least equal to a supramax response threshold indicating muscle relaxation has succeeded to a level in which the patient can be safely extubated;
based on the first muscle responses being at least equal to the supramax response threshold, selecting the submaximal stimulus current for the subsequent series of stimulations; and
based on the first muscle responses being less than the supramax response threshold, selecting the supramaximal stimulus current for the subsequent series of stimulations;
applying, by the electrode, the subsequent series of stimulations at the selected one of the supramaximal stimulus current and the submaximal stimulus current to the nerve of the patient and measuring muscle responses thereto;
comparing the muscle responses to the subsequent series of stimulations to a first threshold; and
based on the muscle responses to the subsequent series of stimulations being below the first threshold, generating an alarm.
|