| CPC A61B 5/1102 (2013.01) [A61B 5/0004 (2013.01); A61B 5/024 (2013.01); A61B 5/02438 (2013.01); A61B 5/0255 (2013.01); A61B 5/026 (2013.01); A61B 5/05 (2013.01); A61B 5/11 (2013.01); A61B 5/1126 (2013.01); A61B 5/242 (2021.01); A61B 5/243 (2021.01); A61B 5/4875 (2013.01); A61B 5/681 (2013.01); A61B 5/6824 (2013.01); A61B 5/7221 (2013.01); A61B 5/725 (2013.01); A61B 5/7257 (2013.01); A61B 5/7278 (2013.01); A61B 5/742 (2013.01); A61B 5/746 (2013.01); A61B 5/7475 (2013.01); A61B 5/4866 (2013.01); A61B 2560/0214 (2013.01); A61B 2562/0219 (2013.01); A61B 2562/0223 (2013.01); A61B 2562/164 (2013.01); A61B 2562/18 (2013.01)] | 12 Claims |
|
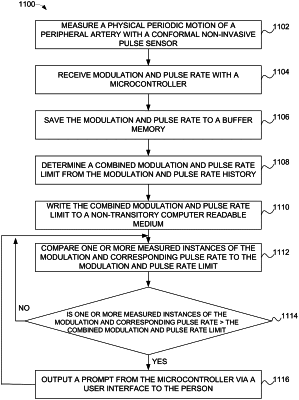
1. A method for monitoring the hydration of a person, comprising:
measuring a pulse at a peripheral artery with a pulse sensor to determine pulse data;
outputting the pulse data as a pulse data set;
receiving the pulse data set with a programmable hardware device;
writing the pulse data set to a memory device as an instant in an arterial pulsation history;
reading the arterial pulsation history;
determining, with a microcontroller, at least one limit, including a pulse wave modulation value corresponding to a difference or ratio between systolic peak and diastolic hump in expansion of the peripheral artery based on the pulse sensor, from the arterial pulsation history;
writing the at least one limit to a non-transitory computer readable medium;
receiving one or more new pulse data sets;
calculating at least one new variable value from the one or more new pulse data sets;
comparing, with the programmable hardware device, the at least one new variable value to the at least one limit; and
outputting a prompt from the microcontroller via a user interface to the person if a predetermined number of instances of the at least one new variable value falls outside the at least one limit.
|