| CPC A61B 5/0261 (2013.01) [A61B 5/0077 (2013.01); A61B 5/412 (2013.01); G06T 7/0012 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30104 (2013.01)] | 8 Claims |
|
1. A method for measurements and calculations of a microcirculatory high-velocity blood flow, comprising the following steps:
step 1: defining the microcirculatory high-velocity blood flow as a microcirculation manifestation of a macro-hemodynamic high output-low resistance phenomenon in a resting state, and setting a blood flow velocity of higher than 1,000 μm/s in an arteriole, a venule, and a true capillary exchange network of a microcirculatory capillary circuitous channel as an initial threshold for the microcirculatory high-velocity blood flow;
step 2: using a microcirculation observation device to select 3 to 5 observation regions at a sublingual mucosa or any other part of a body that allows microcirculation observation and recording videos of the 3 to 5 observation regions; comparing the videos of the 3 to 5 observation regions, selecting a video with a highest blood flow velocity from the videos with blood vessels with blood flow velocity higher than 1,000 μm/s as a high-velocity blood flow candidate sample, and saving the high-velocity blood flow candidate sample in a sample database; and then in the high-velocity blood flow candidate sample selecting a blood vessel with a highest blood flow velocity as a candidate blood vessel sample of the high-velocity blood flow candidate blood vessel sample, without considering a diameter of the blood vessel; and
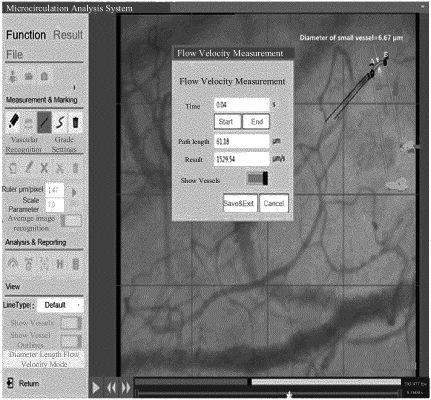
step 3: tracking a trajectory of RBCs, WBCs, or plasma particles in the microcirculatory high-velocity blood flow on a display screen, calculating a traveling distance and a traveling time of the RBCs, the WBCs, or the plasma particles with an aid of a computer, and dividing the traveling distance by the traveling time to calculate an average blood flow velocity of the microcirculatory high-velocity blood flow.
|