| CPC A61B 5/0261 (2013.01) [A61B 5/4064 (2013.01); A61B 2562/0238 (2013.01); A61B 2562/04 (2013.01)] | 31 Claims |
|
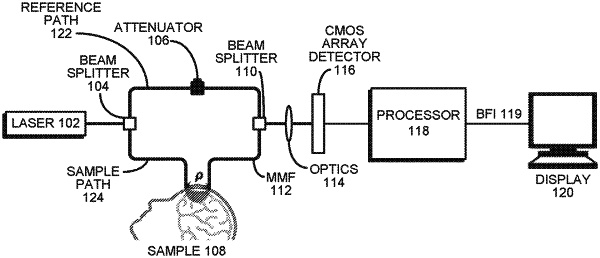
1. A method for non-invasively analyzing blood flow in a sample of living tissue, comprising:
obtaining narrow-band light from a temporally coherent source;
splitting the obtained narrow-band light between a reference path and a sample path;
multiply scattering light from the sample path by passing the light through the sample;
recombining light from the reference path and the multiply scattered light from the sample path;
using a sensor array to detect an interference pattern resulting from the recombination; and
analyzing signals from the sensor array to determine a blood flow in the sample.
|