| CPC H01L 31/1105 (2013.01) [H01L 31/109 (2013.01); H01L 31/1816 (2013.01)] | 19 Claims |
|
10. A method of forming a voltage tunable solar-blind UV detector comprising:
forming a vertical bipolar transistor structure;
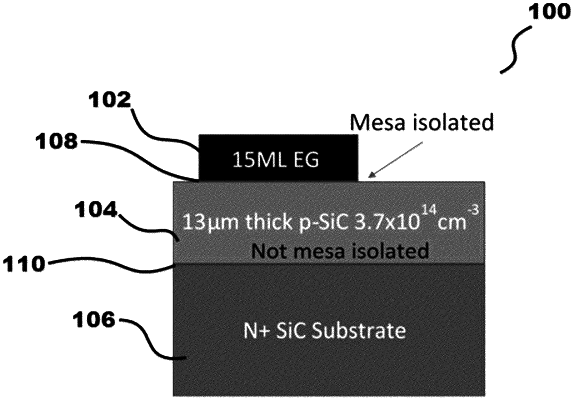
growing a p-SiC epilayer on an n+SiC substrate layer substrate via a CVD reactor;
growing an epitaxial graphene top electrode layer on the p-SiC epilayer by selective etching of
Si from SiC using a Tetrafluorosilane gas precursor;
vertically stacking the epitaxial graphene top electrode layer, intermediate p-SiC epilayer and the n+SiC substrate layer to form an:
epitaxial graphene/SiC heterojunction-based;
voltage tunable;
solar-blind UV detector; and
applying a bias voltage to the epitaxial graphene top electrode layer to shift a peak wavelength responsivity from 320 nm to less than 250 nm dependent upon the bias voltage applied.
|