| CPC G06F 3/015 (2013.01) | 18 Claims |
|
1. A method comprising:
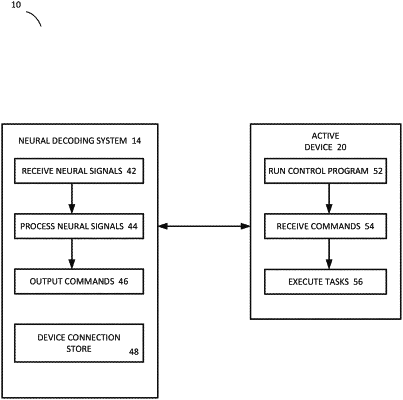
starting an instance of a control program on a device, wherein the device is in communication with a neural decoding system that receives neural signals from a user;
receiving, from the neural decoding system, a command to complete a task, wherein the command is based on the neural signals;
determining whether the device is active;
when the device is active, executing the task on the device based on the command;
starting another instance of the control program on another device, wherein the other device is in communication with the neural decoding system that receives neural signals from the user;
receiving, from the neural decoding system, a request to switch control from the device to the other device;
switching, by the neural decoding system, control from the device to the other device;
sending, from the device, an instruction to the neural decoding system and the other device indicating control is switched;
receiving, from the neural decoding system, another command to complete another task, wherein the other command is based on the neural signals;
determining whether the other device is active; and
when the other device is active, executing the other task on the other device based on the other command.
|