| CPC G05B 19/41875 (2013.01) [G05B 2219/37591 (2013.01)] | 14 Claims |
|
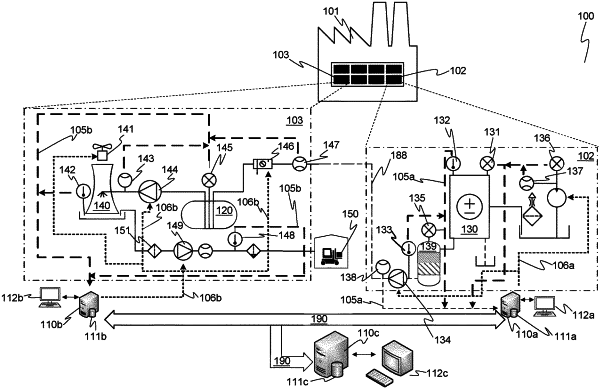
1. A method for monitoring a plant comprising a plurality of sensors, and one or more functionally connected processing units, comprising:
providing, at any of the one or more processing units, time-series residual data of a sensor object; the sensor object being a group of at least some of the sensors from the plurality of sensors, and wherein the residual data comprises, for each of the sensors of the sensor object, a residue signal which is a difference between the sensor's measured output and the sensor's expected output,
monitoring, via any of the one or more processing units, a level signal; wherein the level signal is indicative of a collective time-based variation of the time-series residual data,
monitoring, via any of the one or more processing units, an association signal; wherein the association signal is indicative of the variation and/or association structure of the time-series residual data,
generating, via any of the one or more processing units, an anomaly event signal when at a given time a value of the level signal and/or a value of the association signal changes from an expected value of the respective signal at that given time, and
detecting, via any of the one or more processing units, a drift in the output signal a sensor; wherein the sensor is among the at least some of the sensors, and wherein the drift is computed from historical time series data of the sensor, the historical data of the sensor being from a time period that is at least 1 week long, and wherein the drift is detected by computing the strength, smoothness and currentness of the historical data of the sensor.
|