| CPC B60W 30/09 (2013.01) [B60W 30/0956 (2013.01); G05D 1/0088 (2013.01); G05D 1/0214 (2013.01); G05D 1/0217 (2013.01); G05D 1/0274 (2013.01); G06V 20/58 (2022.01); G05D 2201/0213 (2013.01)] | 24 Claims |
|
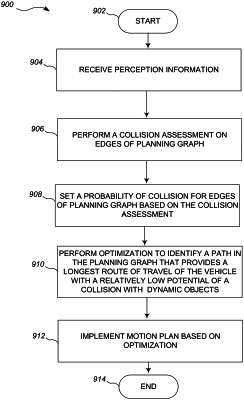
1. A method of operation in a processor-based system to determine paths for vehicles via planning graphs, where each planning graph respectively comprises a plurality of nodes connected by edges, each node which represents, implicitly or explicitly, time and variables that characterize a state of a vehicle which operates in an environment and which environment includes one or more dynamic objects, and each edge represents a transition between a respective pair of nodes, the method comprising:
receiving perception information that represents the environment in which the vehicle operates;
performing a collision assessment on each edge of two or more of the edges of a planning graph;
for each of two or more edges of the planning graph, setting a respective probability of collision for a respective edge of the two or more edges based at least in part on the collision assessment on the respective edge, wherein setting a respective probability of collision for the respective edge for each of two or more edges of the planning graph based at least in part on the collision assessment includes setting a respective probability of collision for each of two or more edges of the planning graph based at least in part on a predicted trajectory of the one or more dynamic objects that is based at least in part on a change in a trajectory of the vehicle;
performing an optimization on the edges of a resulting planning graph, each of the edges having the respective probability of collision that was set therefor, to identify a path in the resulting planning graph that provides a longest route of travel of the vehicle in two-dimensional or three-dimensional space in the environment in which the vehicle operates; and
implementing a motion plan based at least in part on the optimization.
|