| CPC B29C 70/30 (2013.01) [B22F 7/064 (2013.01); B22F 10/00 (2021.01); B22F 10/20 (2021.01); B22F 12/90 (2021.01); B29C 64/147 (2017.08); B29C 64/232 (2017.08); B29C 64/295 (2017.08); B29C 64/307 (2017.08); B29C 64/393 (2017.08); B29C 67/08 (2013.01); B33Y 10/00 (2014.12); B33Y 30/00 (2014.12); B33Y 40/00 (2014.12); B33Y 70/00 (2014.12); C22C 47/025 (2013.01); C22C 47/20 (2013.01); C22C 49/14 (2013.01); B22F 2003/1051 (2013.01); B22F 3/24 (2013.01); B22F 7/04 (2013.01); B22F 2007/042 (2013.01); B22F 2007/045 (2013.01); B22F 7/08 (2013.01); B22F 10/10 (2021.01); B22F 2998/10 (2013.01); B22F 2999/00 (2013.01); B29C 70/528 (2013.01); B32B 15/00 (2013.01); B33Y 40/20 (2020.01); B33Y 50/02 (2014.12); B33Y 70/10 (2020.01); C22C 2200/02 (2013.01); C22C 2200/06 (2013.01)] | 31 Claims |
|
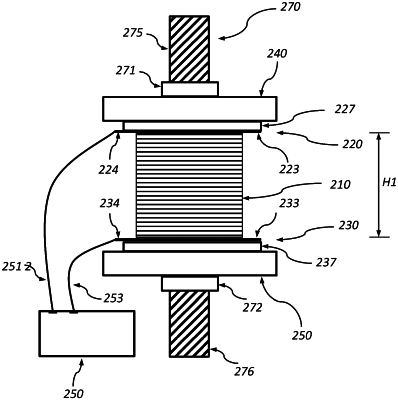
1. A method for resistive heating usable in composite-based additive manufacturing, comprising:
providing a stack of substrate sheets that have been applied with powder;
placing the stack between electrode assemblies of a compression device;
compressing the stack at room temperature to a first height H1;
applying a current between the electrode assemblies to heat the stack to a first target temperature T1;
compressing the stack to an intermediate height that is less than H1 but greater than a final desired compression height H;
applying a current between the electrode assemblies to thereby heat the stack to a temperature T at which the powder changes state to a converted material;
compressing the stack to the final desired compression height H;
cooling the stack; and
removing the cooled, compressed stack from the compression device.
|