| CPC B25J 9/1669 (2013.01) [B25J 9/1605 (2013.01); B25J 9/1633 (2013.01)] | 4 Claims |
|
1. A method for generating a novel impedance configuration for a three-degree-of-freedom (3DOF) robotic leg, comprising:
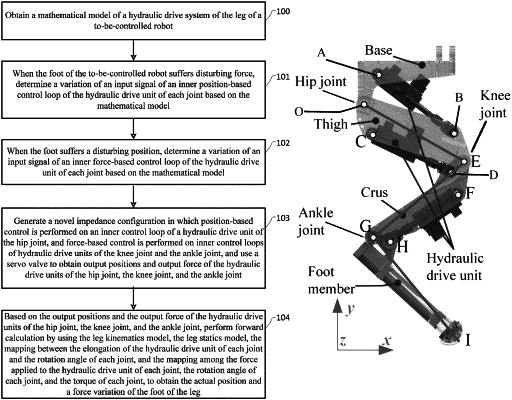
obtaining a mathematical model of a hydraulic drive system of the leg of a to-be-controlled robot, wherein the mathematical model comprises a leg kinematics model, a leg statics model, a leg dynamics model, a leg impedance characteristic model, a mapping between an elongation of a hydraulic drive unit of each joint of the leg and a rotation angle of each joint of the leg, and a mapping among force applied to the hydraulic drive unit of each joint, the rotation angle of each joint, and a torque of each joint; and wherein the leg comprises a hip joint, a knee joint, and an ankle joint;
determining, when a disturbing force is applied to a foot of the to-be-controlled robot, a variation of an input signal of an inner position-based control loop of a hydraulic drive unit of each joint based on the mathematical model;
determining, when the foot is in a disturbed position, a variation of an input signal of an inner force-based control loop of the hydraulic drive unit of each joint based on the mathematical model;
generating the novel impedance configuration in which position-based control is performed on an inner control loop of a hydraulic drive unit of the hip joint, and force-based control is performed on inner control loops of hydraulic drive units of the knee joint and the ankle joint, and using a servo valve to obtain output positions and output force of the hydraulic drive units of the hip joint, the knee joint, and the ankle joint; and
based on the output positions and the output force of the hydraulic drive units of the hip joint, the knee joint, and the ankle joint, performing forward calculation by using the leg kinematics model, the leg statics model, the mapping between the elongation of the hydraulic drive unit of each joint and the rotation angle of each joint, and the mapping among the force applied to the hydraulic drive unit of each joint, the rotation angle of each joint, and the torque of each joint, to obtain an actual position and a force variation of the foot of the leg.
|