| CPC G10L 19/0208 (2013.01) [G10L 19/20 (2013.01); G10L 25/18 (2013.01); G10L 25/21 (2013.01)] | 19 Claims |
|
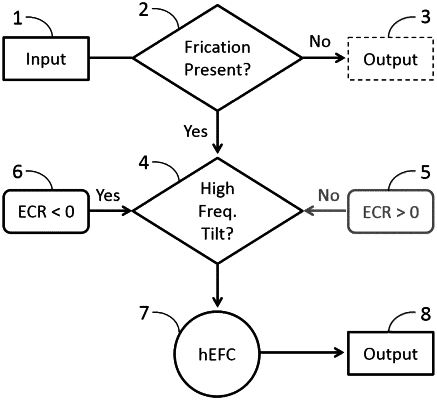
1. A method of audio signal processing comprising:
(a) receiving an audio signal input via a digital signal processor, wherein the audio signal input includes a speech sound;
(b) detecting a high-frequency energy of the speech sound via a detector of the digital signal processor to determine whether frication is present in the audio signal input;
(c) when frication is present in the audio signal input, classifying the audio signal input into two or more speech sound classes, wherein the classification of the audio signal input includes:
A) comparing a band-pass filtered energy of the audio signal input to a high-pass filtered energy of the audio signal input via the digital signal processor;
B) selecting a form of the input-dependent frequency remapping function based on the comparison of the hand-pass filtered enercw and the high-pass filtered energy, wherein the form of the input-dependent frequency remapping function is at least one of:
(i) compressive in the mid frequencies and expansive in the high frequencies, or
(ii) expansive in the mid frequencies and compressive in the high frequencies; and
C) selecting an expansive compression ratio (ECR) based on the selected form of input-dependent frequency remapping function;
(d) upon classifying the audio signal input into two or more speech sound classes, initiating a Hybrid Expansive Frequency Compression (hEFC), wherein the hEFC includes re-coding one or more input frequencies of the speech sound via an input-dependent frequency remapping function to generate one or more output frequencies, wherein the output frequencies are at least one of:
(A) first compressive and then expansive, or
(B) first expansive and then compressive; and
(e) generating an output signal from the output frequencies, wherein the output signal is a representation of the audio signal input having a decreased sound frequency.
|