| CPC G01S 7/4911 (2013.01) [G01S 7/4815 (2013.01); G01S 7/4913 (2013.01); G01S 7/4917 (2013.01); G01S 13/347 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
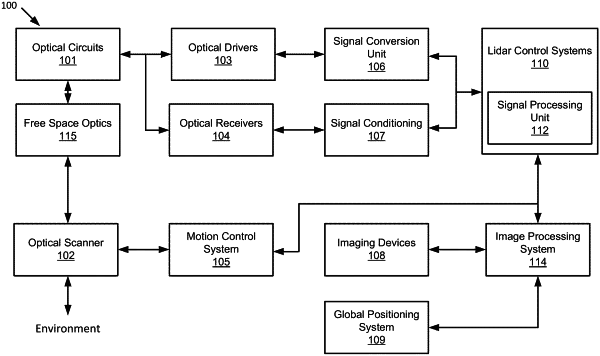
1. A light detection and ranging (LIDAR) system, comprising:
an optical source to emit a corresponding plurality of optical beams with synchronized chirp rates and synchronized chirp durations, wherein the plurality of optical beams are each tuned to produce regions of constructive and destructive interference into a combined optical beam;
a first optical component to form a phase-locked loop to correct nonlinearities detected in the plurality of optical beams;
a second optical component to transmit the combined optical beam toward a target environment and to receive a target return signal; and
a third optical component to downconvert the target return signal to a plurality of fixed frequency downconverted target return signals each comprising a target range component and a target velocity component.
|