| CPC F25D 29/006 (2013.01) [F25D 23/065 (2013.01); F25D 2201/126 (2013.01); F25D 2201/14 (2013.01); F25D 2500/04 (2013.01); F25D 2700/12 (2013.01); F25D 2700/14 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A method of measuring insulation performance in a vacuum insulated cabinet structure, the method comprising the steps of:
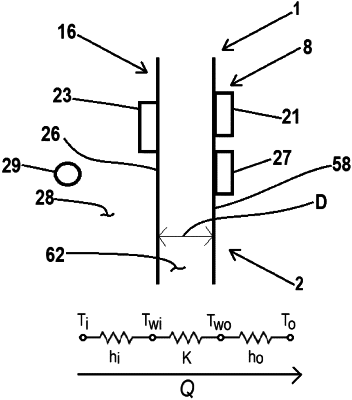
providing a refrigerator having a vacuum insulated cabinet structure with a storage compartment and an insulating space having a thickness, a first sensor positioned on an interior wall of the storage compartment, a second sensor positioned on an exterior wall of the vacuum insulated cabinet structure, a third sensor positioned within the storage compartment, and a controller operably coupled to the first, second and third sensors;
sensing a first temperature level of the interior wall of the storage compartment using the first sensor;
sensing an ambient temperature level within the storage compartment using the third sensor;
sensing a second temperature level of the exterior wall of the storage compartment using the second sensor;
calculating an overall heat transfer coefficient (Q) using the ambient temperature level, the first temperature level, and a convective heat transfer coefficient for the interior wall of the storage compartment;
calculating a temperature differential between the second temperature level and the first temperature level;
determining a conductivity level (K) using the temperature differential, the overall heat transfer coefficient (Q) and the thickness of the insulating space; and
determining a pressure level (P) within the insulating space using the conductivity level (K).
|