| CPC A61B 5/1495 (2013.01) [A61B 5/14532 (2013.01); A61B 5/7203 (2013.01); A61B 5/7275 (2013.01); A61B 5/7278 (2013.01)] | 18 Claims |
|
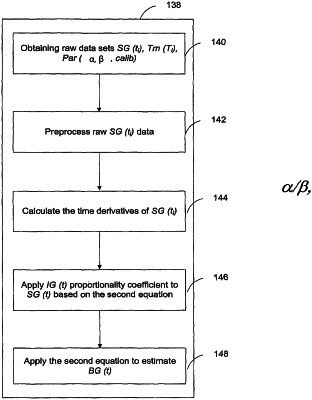
1. A method of improving accuracy of an analyte sensor by accounting for a difference caused by a physiological time lag between a blood glucose value and an interstitial fluid glucose value, the method comprising:
receiving raw output from the analyte sensor, wherein the raw output comprises a plurality of data sets;
preprocessing the plurality of data sets;
obtaining an initial calibration of the analyte sensor; and
determining an estimated blood glucose value from the preprocessed plurality of data sets using the initial calibration of the analyte sensor, wherein the estimated blood glucose value is based on one or more interstitial fluid glucose proportionality coefficients and a time derivative of the raw output, wherein the estimated blood glucose value is indicative of a real-time estimated blood glucose value.
|