| CPC A61B 5/032 (2013.01) [A61B 5/6864 (2013.01); A61B 2562/0247 (2013.01)] | 29 Claims |
|
1. A cerebrospinal-fluid-pressure-measuring device, comprising:
a pressure gauge including:
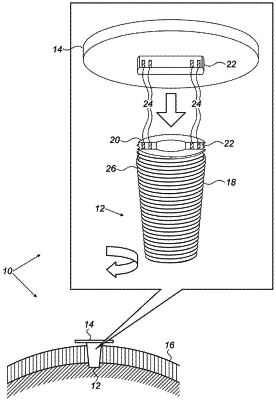
a hollow cylindrical body configured for inserting through a skull and having a lower end, an upper end, a length measure from the lower end to the upper end extending in a length direction, an inner surface extending along the length direction of the hollow cylindrical body, an outer surface, and a cavity defined by the inner surface from the lower end towards the upper end, wherein the upper end of the hollow cylindrical body includes a drive or bolt head to aid in screwing the pressure gauge into the skull for fastening therein;
a membrane attached to the lower end so as to at least partially seal the cavity, the membrane being configured to move under a pressure of cerebrospinal fluid within the skull; and
a plurality of coils including a stationary coil and a moving coil, the stationary coil being (i) disposed in the cavity of the hollow cylindrical body, (ii) connected to the inner surface of the hollow cylindrical body so as to remain stationary with respect to the hollow cylindrical body, and (iii) extending along the length direction along the inner surface, the moving coil being disposed in the cavity of the hollow cylindrical body, extending along the inner surface, and directly connected to the membrane so that the moving coil moves with respect to the stationary coil when the membrane moves under the pressure from the cerebrospinal fluid, one of the stationary coil or the moving coil being configured as a transmitting coil and another of the stationary coil or the moving coil being configured as a receiving coil; and
a control unit comprising a memory and a processor configured to contact the upper end of the hollow cylindrical body so as to apply an input signal to the transmitting coil and receive an output signal from the receiving coil in response to the input signal, and to generate an indication of the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid responsively to the output signal.
|