| CPC H04L 63/1416 (2013.01) [G06N 5/04 (2013.01); G06N 20/00 (2019.01)] | 9 Claims |
|
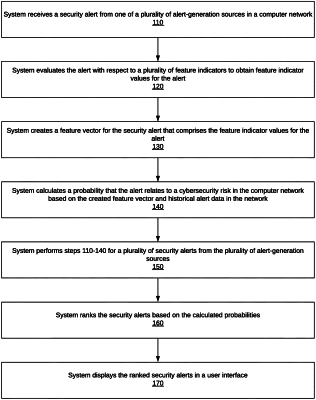
1. A method, performed by a computer system, for ranking computer network security alerts from multiple sources, the method comprising:
(a) receiving a security alert from one of a plurality of alert-generation sources in a computer network;
(b) evaluating the security alert with respect to a plurality of feature indicators to obtain feature indicator values for the security alert;
(c) creating a feature vector for the security alert that includes the feature indicator values for the security alert;
(d) calculating a probability that the security alert relates to a cybersecurity risk in the computer network based on the created feature vector and historical alert data in the network, wherein the probability is a Bayes probability calculated as a function of the probability of seeing the feature vector with respect to a cybersecurity risk and the probability of seeing the feature vector with respect to legitimate or low-interest activity, wherein calculating the probability of seeing the feature vector with respect to a cybersecurity risk and the probability of seeing the feature vector with respect to legitimate or low-interest activity comprises: dividing the feature vector for the alert into a plurality of non-overlapping subsets to create a plurality of subset feature vectors, for each subset feature vector, calculating a probability of seeing the subset feature vector with respect to a cybersecurity risk and a probability of seeing the subset feature vector with respect to legitimate or low-interest activity, and calculating the product of the probabilities calculated for the subset feature vectors to obtain the probability of seeing the feature vector with respect to a cybersecurity risk and the probability of seeing the feature vector with respect to legitimate or low-interest activity;
(e) performing steps (a)-(d) for a plurality of security alerts from the plurality of alert-generation sources;
(f) ranking the security alerts based on the calculated probabilities; and
(g) displaying the ranked security alerts, wherein the alert ranking includes alerts from a plurality of alert-generation sources.
|