| CPC H03K 17/14 (2013.01) [H03K 17/04 (2013.01); H03K 17/0412 (2013.01); H03K 17/28 (2013.01); H02M 1/088 (2013.01)] | 7 Claims |
|
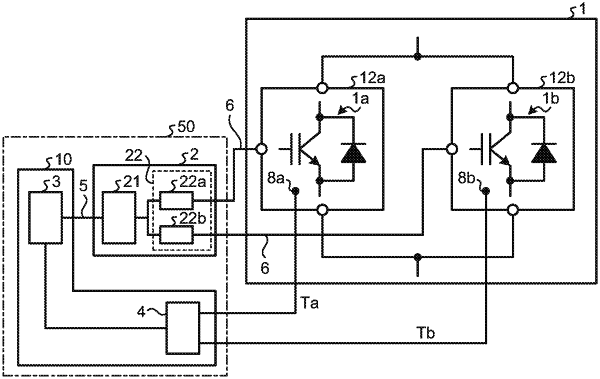
1. A parallel driving device to drive a plurality of parallel-connected semiconductor elements, the parallel driving device comprising:
a controller to detect a temperature difference between the semiconductor elements on a basis of detected values provided by temperature sensors, the temperature sensors detecting temperatures of the individual semiconductor elements, and to generate a control signal for changing a timing at which to turn on a first semiconductor element specified from the semiconductor elements on the basis of the temperature difference; and
a driving circuit to generate a first driving signal for driving the semiconductor elements, and to generate a second driving signal that is the first driving signal delayed on the basis of the control signal and apply the second driving signal to the first semiconductor element, wherein
the driving circuit is a driving circuit having a voltage variable function or a constant-current driving circuit.
|