| CPC G16H 50/80 (2018.01) [A47L 11/4011 (2013.01); G06V 40/161 (2022.01); G06V 40/23 (2022.01); G16H 50/30 (2018.01); A47L 2201/04 (2013.01); A47L 2201/06 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
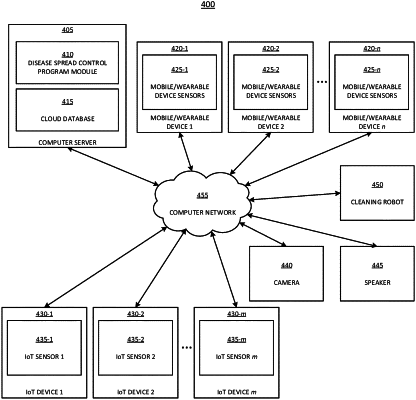
1. A computer-implemented method comprising:
obtaining, by a computing device, information of a person from one or more remote wearable devices of the person via a computer network;
determining, by the computing device, a health status of the person by analyzing the information of the person;
determining, by the computing device, that the person is sick based on the health status;
in response to determining that the person is sick, obtaining digital images of the person from a camera via the computer network;
determining, by the computing device, body movements of the person determined to be sick by analyzing the digital images;
determining, by the computing device, that the person determined to be sick performed a germ-transmitting activity based on the body movements; and
deploying, by the computing device, a remote cleaning robot to clean a potentially contaminated area based on the determining that the person determined to be sick performed the germ-transmitting activity.
|