| CPC G16H 50/30 (2018.01) [A61B 5/0002 (2013.01); A61B 5/4842 (2013.01); A61B 5/7225 (2013.01); A61B 5/7275 (2013.01); G16H 50/20 (2018.01)] | 11 Claims |
|
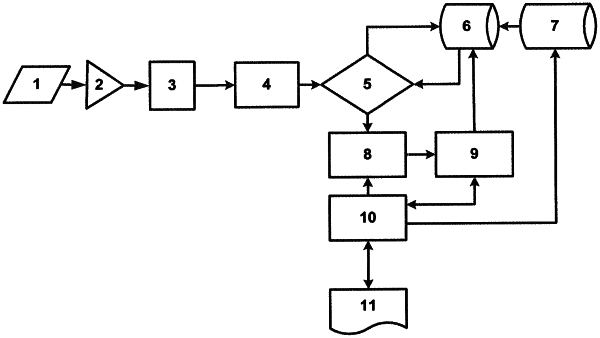
1. A method of automatic diagnosing conditions of an object comprising:
passively receiving and recording a wave electromagnetic signal from the object's surface,
performing spectral-dynamic conversions of the signal and comparing them with ethologic samples,
processing diagnostic operations, including determining spectral-dynamic matchings of the processed signal to at least one spectral-dynamic sample from the group of samples, being a reference for the object's status to be diagnosed, and
defining a degree of matching by averaging out from degrees of matching of processed spectral-dynamic samples with each sample in a group, and
in the case when the degree of matching is below a first specified value, deciding the conclusion of absence of the status being diagnosed and displayed, and
in the case when the degree of matching is equal or is higher than the first specified value, matching the processed signal to at least one more spectral-dynamic sample, being referential to the same status, and
in the case when the degree of matching is established below a second specified value, deciding a presence of risk of an onset of the status to be diagnosed and displayed, and
in the case when the degree of matching is determined to be equal or higher than a third specified value, matching of the processed signal is performed to at least one more successive spectral-dynamic sample being referential to the same status, and
in the case when the degree of matching is determined to be below the third specified value, deciding whether the conclusion of a presence of a latent phase of the status progress is indicated, and when the degree of matching is determined to be equal to or higher than said specified value, deciding the conclusion of a presence of a manifested phase of the status to be diagnosed, and displaying it; and
performing an additional diagnostic test by forming a wave signal of a recognized sample, with this recognized sample being inverted in case it belongs to a hyperenergetic type, converting the hyperenergetic type to an analogue form, amplifying it, feeding it to a testing electrode located on the object's surface and testing an effect being produced, and then determining the relevance of the status to be diagnosed by either by the rate response time or biofeedback response time.
|