| CPC G16H 50/20 (2018.01) [A61B 5/0042 (2013.01); A61B 5/02042 (2013.01); A61B 5/4064 (2013.01); A61B 6/501 (2013.01); A61B 8/0808 (2013.01); G16H 30/20 (2018.01); G16H 50/30 (2018.01); A61B 5/0535 (2013.01); A61B 5/055 (2013.01); A61B 6/032 (2013.01); A61B 8/488 (2013.01); A61B 2576/00 (2013.01); A61B 2576/026 (2013.01); G01N 2800/2871 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30004 (2013.01)] | 28 Claims |
|
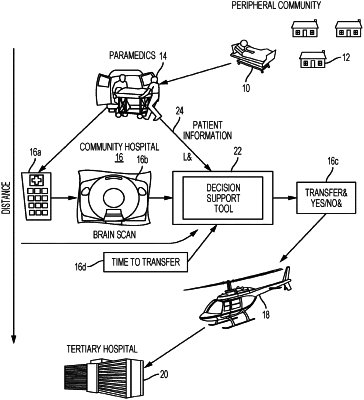
1. A method to determine that a stroke patient should be transferred from a first treatment facility to a second treatment facility capable of performing endovascular therapy, the method comprising:
receiving clinical data for the stroke patient at the first treatment facility;
receiving imaging data from one or more imaging modalities for the stroke patient at the first treatment facility and determining an image profile for the stroke patient;
inputting the clinical data for the stroke patient and the image profile into a computer device;
determining, by the computer device, an estimated transfer time from the first treatment facility to the second treatment facility capable of performing endovascular therapy, an estimated treatment time at the second treatment facility, and a total time to treatment based on the estimated transfer time and the estimated treatment time;
determining, by the computer device, a patient assessment profile from the image profile, wherein the patient assessment profile includes an estimate of an amount of brain tissue that may be irreversibly infarcted at the total time to treatment;
determining, by the computer device, a probability of an acceptable outcome based on the patient assessment profile and whether the patient is transferred to the second treatment facility capable of performing endovascular therapy; and
outputting, by the computer device, based on a plurality of decisive factors, a decision to transfer the patient to the second facility capable of performing endovascular therapy, wherein the computer device is configured to provide automatic decision support by implementing machine learning techniques based on expert physician data, the clinical data, and the imaging data, wherein the plurality of decisive factors include a perfusion threshold value, the patient assessment profile, and an estimated time to reperfusion.
|