| CPC G06V 20/584 (2022.01) [G01C 21/32 (2013.01); G06N 3/08 (2013.01); H04W 4/44 (2018.02)] | 14 Claims |
|
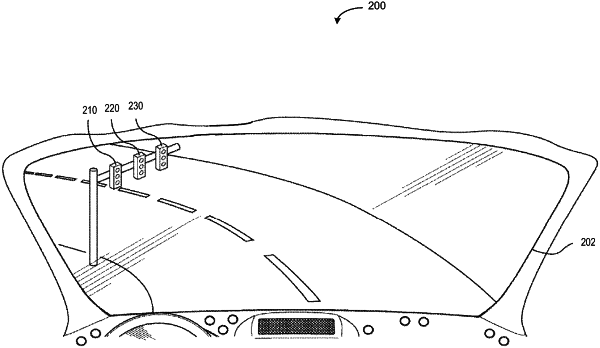
1. A method, comprising:
predicting a state of a traffic signal using a model;
obtaining vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I)-based information regarding the state of the traffic signal;
comparing the predicted state of the traffic signal with the V2I-based information regarding the state of the traffic signal;
in response to a determination that the predicted state of the traffic signal is inconsistent with that of the V2I-based information regarding the state of the traffic signal, updating training data by saving data related to the state of the traffic signal; and
training the model used to predict the state of the traffic signal using the updated training data.
|