| CPC G06T 11/001 (2013.01) [G06T 7/90 (2017.01); G06T 15/80 (2013.01); G06T 19/20 (2013.01); G06T 5/008 (2013.01); G06T 2200/04 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10028 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10056 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30096 (2013.01)] | 3 Claims |
|
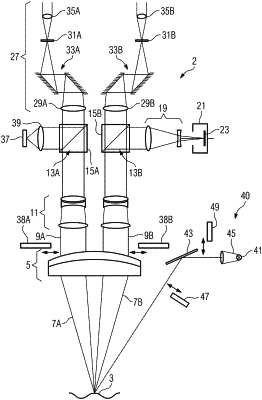
1. A method for correcting a shading in a digital image of a three-dimensional observation object obtained with an optical observation device, the optical observation device including a first image sensor and a second image sensor, the first image sensor being arranged in a first partial beam path defined by the optical observation device and the second image sensor being arranged in a second partial beam path defined by the optical observation device, the three-dimensional observation object being illuminated by illumination light having an intensity distribution, and an inhomogeneity in an image brightness being present in the digital image of the three-dimensional observation object, the method comprising:
ascertaining a topography of the three-dimensional observation object;
correcting the inhomogeneity in the image brightness of the digital image based on the topography of the three-dimensional observation object and the intensity distribution of the illumination light;
embodying the optical observation device to record stereoscopic images, the first image sensor being configured to record a first stereoscopic partial image and the second image sensor being configured to record a second stereoscopic partial image;
ascertaining the topography of the three-dimensional observation object based on the first and second stereoscopic partial images; or
ascertaining the topography of the three-dimensional observation object based on a structured illumination and a distortion of a structure of an illumination in the image of the three-dimensional observation object recorded with the structured illumination.
|