| CPC G06Q 10/0833 (2013.01) [G06F 9/4498 (2018.02)] | 16 Claims |
|
1. A method, comprising:
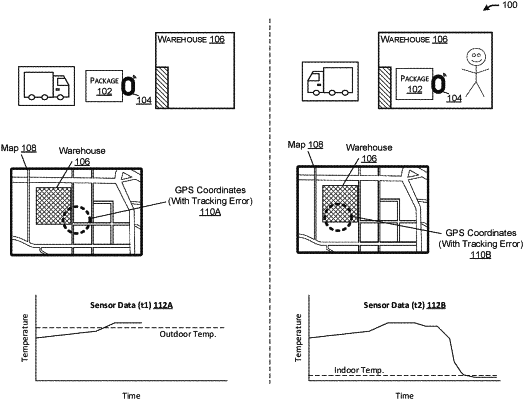
obtaining, by one or more processors of a device, sensor data collected from a tracking device associated with a first asset, wherein the sensor data includes indirect sensor data, and wherein the indirect sensor data includes at least one of environmental and temperature data;
determining, by the one or more processors of the device, asset workflow information associated with the first asset, wherein the asset workflow information indicates an expected workflow associated with the first asset;
training an intelligence engine configured to generate an inference of a status associated with the first asset;
using, by the one or more processors of the device, the intelligence engine to generate an inferred state based on the indirect sensor data and the asset workflow information;
determining, by the one or more processors of the device, the status associated with the first asset based on the inferred state;
storing, by the one or more processors of the device, the status of the first asset in an asset tracking database;
determining historical sensor data associated with the first asset, wherein the historical sensor data includes direct sensor data;
determining, by the one or more processors of the device and based on the historical sensor data, ground truth data for the intelligence engine;
comparing the inferred state and the ground truth data; and
re-training, by the one or more processors of the device, the intelligence engine based on comparing the inferred state and the ground truth data.
|