| CPC G06F 21/31 (2013.01) [G06F 21/16 (2013.01); G06F 21/577 (2013.01); G06F 21/604 (2013.01); G06F 21/6209 (2013.01); G06F 21/6245 (2013.01); G06F 21/6254 (2013.01); G06F 21/6263 (2013.01); G06N 20/00 (2019.01); G06Q 30/0206 (2013.01); G06Q 50/18 (2013.01); G06F 2221/034 (2013.01); G06F 2221/2123 (2013.01); G06F 2221/2141 (2013.01)] | 23 Claims |
|
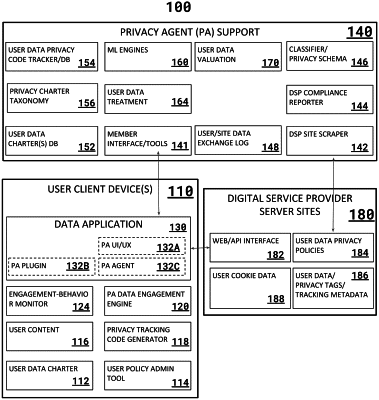
1. A method of implementing privacy protection for a user with an automated security agent controlling online interactions with a digital services provider (DSP) comprising:
a. determining with the automated security agent whether a first digital service provider (DSP) is designated as a white listed entity for the user by a user privacy charter;
wherein the automated security agent designates said first DSP as a white listed entity when the latter is determined to satisfy user enabled access requirements for selected data privacy items;
b. when the first DSP is not designated as a white list entity, causing the automated security agent to generate a set of decoy requests configured for a protocol and format employed by the first DSP;
wherein the automated security agent selectively employs decoy requests on a DSP-by-DSP basis based on a particular DSP's compliance with said user access requirements for said selected data privacy items;
c. presenting both an accurate request containing said user data and one or more decoy requests containing artificial data to said DSP for said user device with the automated security agent when said first DSP is not designated as a white list entity; and
d. processing a first response from the DSP for said accurate request and one or more second responses from the DSP for said one or more decoy requests;
e. communicating at least said first response to the user device;
wherein the user data is intermingled with said artificial data to reduce data tracking and assignability of the selected data privacy items to the user when said first DSP is not designated as a white list entity.
|